
Low Energy Data Centre
Materials for the server room
The main things that we had to keep in mind during the whole design of the server room were the following:
-
Protect the servers from the risks on condensation, and especially from condensation on the ceiling.
-
Insure the cooling of the servers by the most ecological way.
We chose to build our server room with exteriors bricks insulated by lamb’s wool and a cavity. A wall of 40cm is enough to avoid any risk of condensation and guarantee the PassivHaus standard with a U-value of 0.15W/m²K.
We chose the bricks because it has a low embodied energy, local carriers could supply us and it’s fire resistant. Moreover, bricks doesn’t need a lot of maintenance.
Brick is the material with the next lowest amount of embodied energy, 4 times that of wood, then concrete (5 X), plastic (6X), glass (14X), steel (24X) and aluminium (126X) [1]


Fig 1: Bricks + lamb's wool
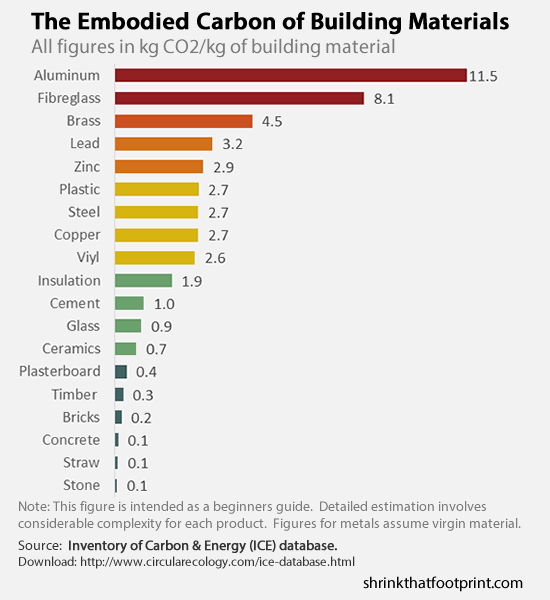
Fig 2: Comparison of materials embodied energy
Regarding the insulator, the choice of Lamb’s wool may appear strange but it’s local, cheaper than the other insulators and it’s ecological: no toxic chemical products in the wool. It also has a low thermal conductivity and it is recyclable at 100%.[2]
Wool batts generally contain 85% wool mixed with 15% polyester.
The cleaning, air laying and thermal bonding processes for lamb’s wool consumes only 14% of the energy used for glass fibre insulation.
The lamb’s wool has a higher resistance to fire than cellulose and cellular plastic insulators because it melts when it comes into contact with an ignition source. It is also treated with fire proofing agent.
Table1 : Comparison of materials properties
References
[1]Ten shades of green. (2014). Embodied Energy. Available: http://www.tenshadesofgreen.org/shade4.html. Last accessed April 2015.
[2]low energy house. (2015). Low Energy House - What is Sheep Wool Insulation?. Available: http://www.lowenergyhouse.com/sheep-wool-insulation.html. Last accessed April 2015.